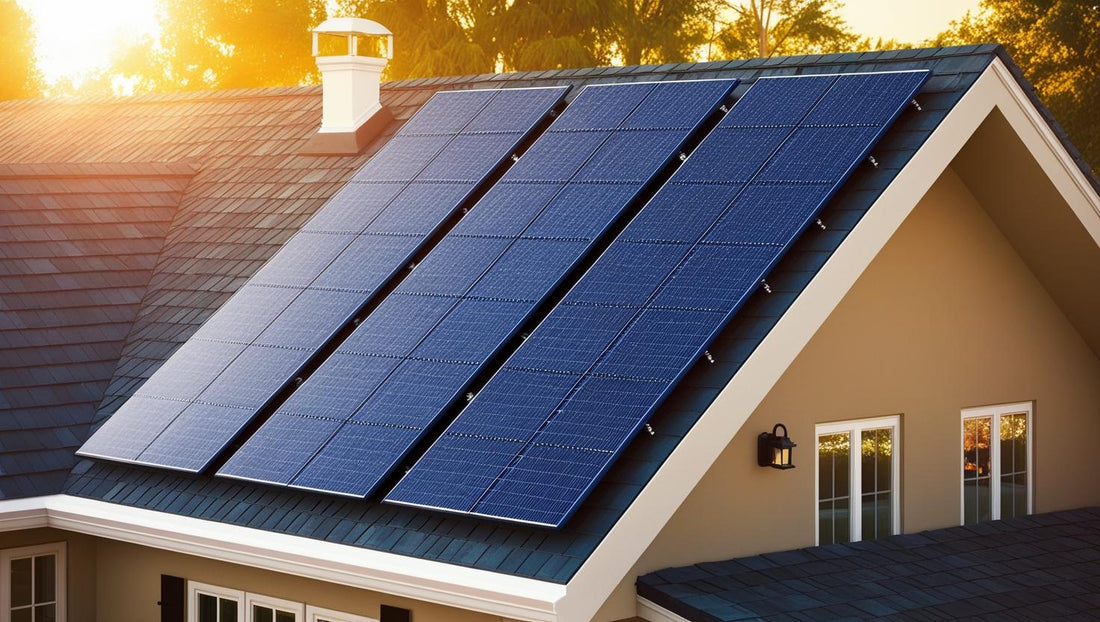
Solar energy has become a popular solution as more people look for ways to save money and reduce their carbon footprint. But if you’re new to the idea, you might wonder: how do solar panels actually power your home? This beginner-friendly guide will explain the basics in simple terms.
What Are Solar Panels?
Solar panels are devices that capture sunlight and turn it into electricity. They are usually made of silicon cells that create an electric current when exposed to sunlight. A group of panels installed together is called a solar array.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
Here’s a step-by-step look at how solar panels power your home:
-
Sunlight Hits the Panels:
The process starts when sunlight hits the solar panels on your roof or yard. -
Electricity Is Generated:
The solar cells in the panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. -
Inverter Changes the Current:
Homes use alternating current (AC) electricity, so the DC power from the panels needs to be converted. This is done by a solar inverter. -
Power Your Home:
Once converted, the AC electricity flows into your home’s electrical system to power your lights, appliances, and other devices. -
Excess Energy:
If your panels produce more electricity than you need, the extra energy can be stored in batteries or sent back to the grid if your utility company allows it.
Key Components of a Solar Power System
To fully understand how solar panels power your home, it helps to know the main parts of the system:
-
Solar Panels: Capture sunlight.
-
Inverter: Converts DC to AC electricity.
-
Battery (Optional): Stores excess energy.
-
Mounting System: Holds panels in place.
-
Meter: Measures your electricity use and production.
Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid Systems
-
Grid-Tied Systems:
These are connected to your local utility grid. You can use solar power when available and rely on the grid when it's not. Extra power can be sent to the grid. -
Off-Grid Systems:
These work independently of the utility grid and often include batteries for storage. They are ideal for remote locations.
How Much Power Can You Get?
The amount of power your solar panels produce depends on factors like:
-
Location: Areas with more sunlight produce more power.
-
Panel Efficiency: Higher-efficiency panels generate more electricity.
-
Angle and Position: Panels should face the sun for maximum exposure.
Benefits of Solar Power
-
Lower Bills: Solar energy can reduce or even eliminate your electricity bills.
-
Eco-Friendly: Solar power reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Low Maintenance: Solar systems usually require little upkeep.
Is Solar Right for You?
Before installing solar panels, consider:
-
Do you have enough sunny space?
-
What is your average electricity use?
-
Are there government incentives or rebates?
Conclusion
Solar panels offer a clean, renewable way to power your home. By understanding the basics—how sunlight becomes electricity—you can make informed decisions about going solar. Whether you choose a simple grid-tied setup or a full off-grid system, solar power is a step toward energy independence and a greener future.