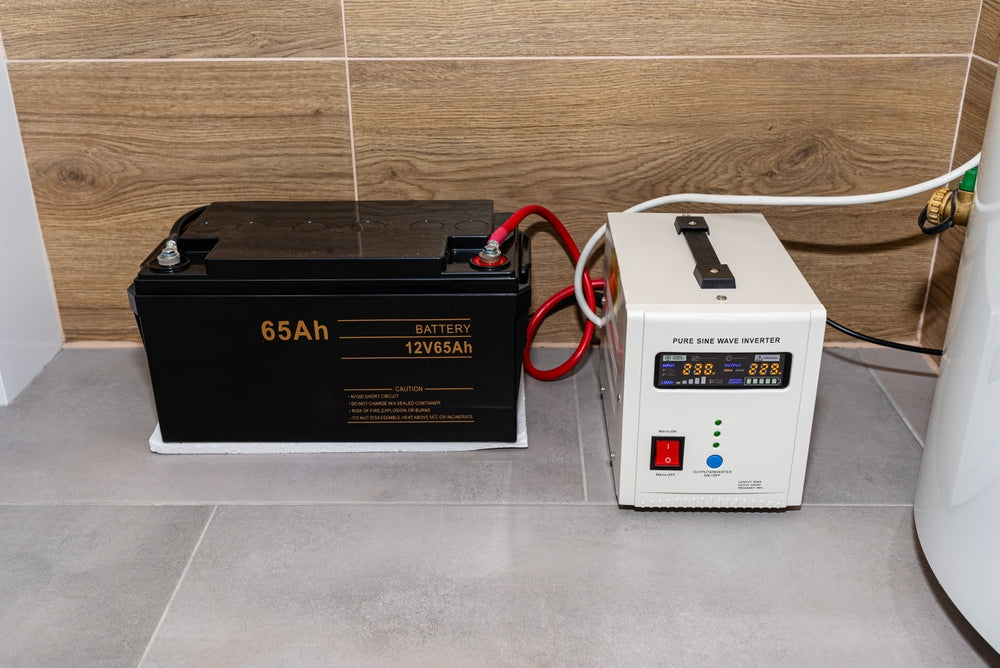
Imagine this: you're in the middle of a critical work presentation, and suddenly the power goes out. Your screen turns black, your files are unsaved, and panic sets in. That’s where a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) comes in your silent shield against power disruptions.
But not all UPS systems are created equal. Whether you’re protecting a home PC, an office server, or sensitive medical equipment, choosing the right type Online, Offline, or Line-Interactive can make all the difference.
Let’s break them down in plain language, so you can choose the best backup power for your specific needs.
What Is a UPS and Why You Need One
More Than Just a Battery Backup
A UPS is a device that supplies backup power when your main electricity fails or fluctuates. But it’s not just about keeping devices turned on. It’s about protecting sensitive electronics from voltage spikes, dips, and surges that can cause lasting damage.
Everyday Examples Where UPS Saves the Day
Think about losing hours of work because your computer shut off mid-task. Or imagine your Wi-Fi cutting out during an emergency call. A UPS prevents these scenarios by giving you those extra precious minutes to save, shut down properly, or ride out short outages seamlessly.
Offline UPS: Basic But Better Than Nothing
How It Works
Also called Standby UPS, this is the simplest type. During normal operation, your devices are powered directly from the wall outlet. When the power fails or voltage dips too low, the UPS switches to battery mode in a split second (usually 5–10 milliseconds).
Best For Light Use
Offline UPS units are budget-friendly and ideal for personal computers, modems, and routers. They’re not designed for highly sensitive equipment but offer solid protection against complete outages and minor surges.
If you only experience occasional blackouts and don’t run mission-critical devices, this option might be all you need.
Line-Interactive UPS: The Reliable Middle Ground
How It Works
Line-Interactive UPS systems still pass power directly to your devices like an Offline UPS, but with a twist: they regulate voltage fluctuations before switching to battery. A built-in automatic voltage regulator (AVR) corrects minor dips and spikes without using the battery.
This makes Line-Interactive UPS systems more efficient, and it extends battery life.
Great for Small Offices and Home Setups
These are perfect for desktop PCs, network gear, gaming setups, and entry-level servers. If you’re in an area with frequent brownouts or voltage instability, a Line-Interactive UPS gives you smoother, uninterrupted performance.
They’re more expensive than Offline models, but still affordable for most households and small businesses.
Online UPS: Ultimate Protection for Critical Systems
How It Works
Online or Double-Conversion UPS systems take power protection to another level. Incoming AC power is converted to DC and then back to clean, regulated AC before reaching your devices. This way, your electronics are always running off the battery/inverter system even when power is "on."
The result? Zero transfer time. Power failure? Voltage fluctuation? You won’t even notice.
Built for Sensitive and Mission-Critical Environments
If you’re managing servers, data centers, hospital equipment, or high-end AV systems, an Online UPS is your best choice. It offers constant, clean, and filtered power, no matter what’s happening on the grid.
However, this level of protection comes at a price both in terms of cost and energy consumption. But for businesses or users who can’t afford even a moment of downtime, it’s worth every penny.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a UPS
1. Power Capacity (VA Rating)
UPS systems are rated in Volt-Amps (VA). To find the right one, calculate the total wattage of devices you plan to protect, then choose a UPS with at least 20–30% more VA than your total load.
2. Battery Runtime
How long do you need your UPS to last during an outage? Most home UPS units give you 5–20 minutes just enough to save your work or power down safely. Larger units for servers may offer 30 minutes or more.
3. Number and Type of Outlets
Make sure the UPS has enough outlets and the right kind (e.g., surge-only vs. battery+surge). Also check for USB ports if you need to power modems or routers.
4. Form Factor and Noise
Will your UPS sit under a desk? Mount in a rack? Some produce fan noise during operation, especially Online models something to consider for home environments.
Maintenance and Monitoring Tips
Keep Your UPS Healthy
UPS systems require occasional upkeep. Replace the battery every 3–5 years, test regularly using self-test functions (many models have this), and keep the unit dust-free.
Use Monitoring Software
Many UPS models come with software or USB/serial interfaces to monitor battery health, power events, and usage stats. Some advanced systems even send you email alerts or integrate with smart home systems.
This adds a layer of transparency and control that’s especially useful for business users.
Final Thoughts: Match the Right UPS to Your Needs
Choosing a UPS isn’t just about picking the biggest or most expensive one it’s about finding a solution that fits your environment. If you’re protecting a home computer or router, a simple Offline UPS may do. For small business networks, a Line-Interactive unit adds smart voltage regulation. And if you’re handling critical infrastructure, go with an Online UPS for uninterrupted protection.
Start with what matters most to you: budget, runtime, sensitivity of your equipment, and outage frequency. Once you answer those questions, the right choice will be clear.
Because in a world where digital work, entertainment, and communication rely on constant power, a well-chosen UPS is more than a backup it’s a lifeline.