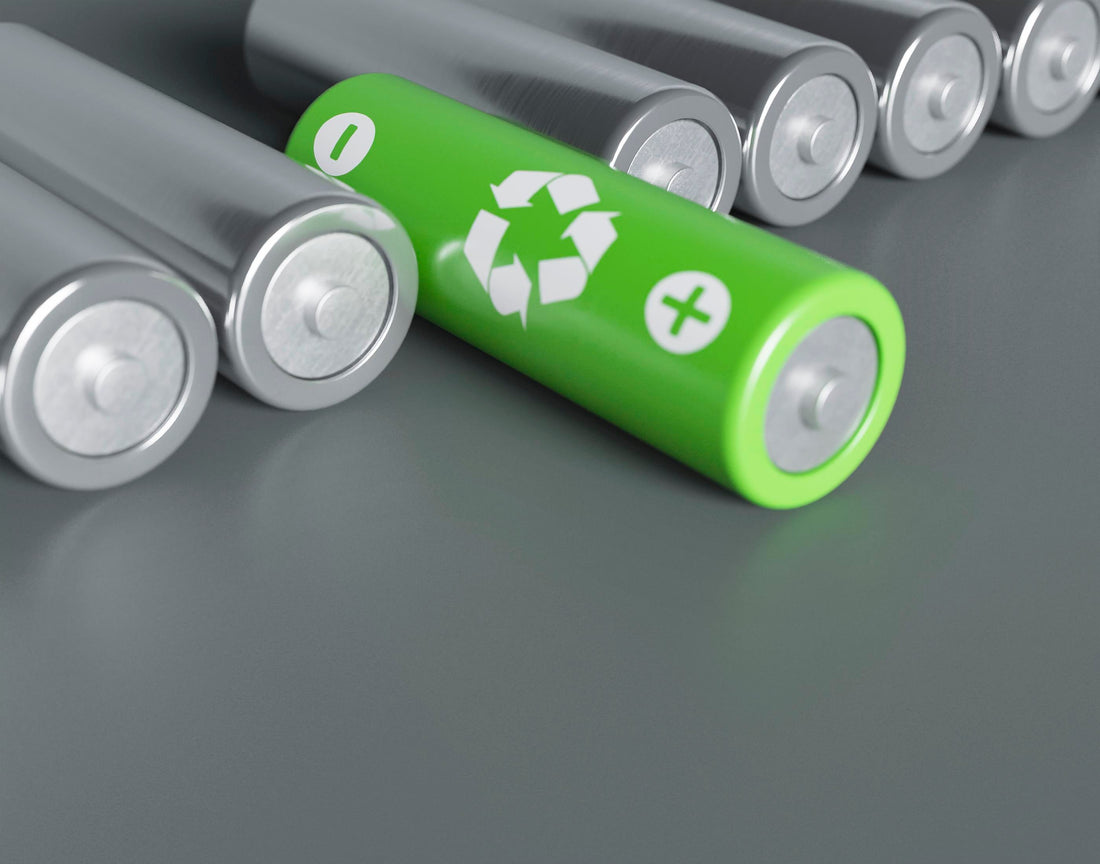
Batteries power many things we use every day. From phones and laptops to cars and solar power systems, batteries are everywhere. But what happens when a battery stops working? Throwing it in the trash is not the right answer. Batteries contain metals and chemicals that can harm the environment if not handled properly.
That is why battery recycling is important. It helps recover useful materials, reduces pollution, and supports the safe reuse of parts. In this guide, we will explain the basics of battery recycling, why it matters, and how to do it the right way.
Why Battery Recycling Matters
Batteries are made from materials like lead, lithium, nickel, and cadmium. These materials can pollute the soil and water if they leak from landfills. Some are also dangerous to human health. When batteries are burned or buried, they can release toxic gases or seep harmful substances into the ground.
By recycling batteries, we prevent these risks. Recycling also saves energy. It takes less energy to reuse metals from old batteries than to mine and process new ones. This helps conserve natural resources and reduces the carbon footprint.
Some batteries contain rare materials that are hard to find. By recycling, we recover these materials and reduce the need for mining. This helps protect the environment and saves money.
Types of Batteries and How to Recycle Them
Not all batteries are the same. Different types need different handling methods. Let us look at the most common types and how they are recycled.
Lead acid batteries are often used in cars, solar power systems, and backup systems. These batteries are among the most recycled items in the world. Almost every part of a lead acid battery can be reused. The lead is melted down and used in new batteries. The acid is treated or turned into water. The plastic case is also recycled. These batteries should always be taken to a battery collection point or service center.
Lithium ion batteries are common in phones, laptops, and electric vehicles. They are powerful but can be dangerous if damaged or exposed to heat. These batteries must be handled carefully. At recycling centers, they are sorted by chemistry and broken down in special facilities. The lithium, cobalt, and other metals are then separated and reused. Never put these batteries in regular trash or curbside recycling bins. Look for e-waste recycling centers or battery drop-off points.
Nickel cadmium and nickel metal hydride batteries are used in older electronics, tools, and some medical equipment. These should be returned to certified recycling centers, as cadmium is a toxic metal. Proper recycling recovers the metals safely.
Alkaline batteries were once hard to recycle, but new systems now allow some centers to accept them. They contain zinc and manganese, which can be reused. Check local rules, as not all areas offer recycling for these batteries.
Button cell batteries are found in watches, hearing aids, and calculators. Some contain mercury or silver. These should always be brought to a special recycling center or pharmacy that accepts them.
How to Prepare Batteries for Recycling
Before you recycle a battery, follow a few simple steps to keep everyone safe.
Remove batteries from the device when possible. If a device has a built-in battery, take the whole item to an e-waste center.
For loose batteries, especially lithium types, place tape over the ends to prevent short circuits or sparks.
Store used batteries in a cool dry place away from heat and direct sunlight.
Do not mix different types of batteries in one container. Keep them separated by type.
Use a clear label or bag if needed to make sorting easier for the recycling center.
Where to Recycle Batteries
Most cities and towns have collection programs for used batteries. These include
-
Local recycling centers
-
Retail stores that sell electronics or batteries
-
Battery collection bins at supermarkets or hardware stores
-
E-waste drives or special disposal events
-
Authorized service centers for car or solar batteries
Check with your local waste authority or city website for the closest and safest option.
Never toss batteries into the regular trash. They can catch fire in garbage trucks or landfills. Always use a safe and approved drop-off location.
Reuse and Second Life of Batteries
In some cases, batteries that no longer hold a full charge can still be reused. This is known as second life. For example, batteries from electric vehicles that are no longer fit for driving can still store energy for solar power systems or other home uses.
Some companies test and rebuild used batteries to give them a second life. These reused batteries may not have full strength but can still perform well for backup systems or low power needs. This helps reduce waste and makes battery systems more affordable.
Tips for Reducing Battery Waste
To lower the number of batteries you need to recycle, try these simple ideas
-
Use rechargeable batteries instead of disposable ones
-
Choose devices with built-in power-saving features
-
Unplug devices when not in use to extend battery life
-
Store batteries in cool places to slow down aging
-
Buy quality batteries that last longer and are easier to recycle
Final Thoughts
Battery recycling is a simple step that has a big impact. It keeps harmful materials out of the environment, saves energy, and supports the reuse of valuable resources. Whether it is a phone battery or a car battery, make sure it ends up in the right place.
By learning how to recycle batteries and using them wisely, we all take a step toward a cleaner and safer future. So the next time a battery dies, do not toss it in the trash. Take it to a recycling center and be part of the solution.