When the power goes out, life comes to a halt. From missing virtual meetings to spoiled groceries, blackouts can be more than just an inconvenience. In today's world, where power equals productivity and comfort, having a reliable home backup generator isn’t a luxury it’s peace of mind. But with so many options on the market, how do you select the right generator for your specific needs?
Let’s walk through everything you need to know from understanding types of generators to evaluating your home’s power requirements so you can make an informed, confident decision.
Understanding Why You Need a Backup Generator
The Reality of Power Outages
Power outages can happen anytime due to storms, infrastructure issues, or overloads. While short outages might be tolerable, prolonged blackouts can interrupt heating, cooling, cooking, and medical devices. That’s why more homeowners are investing in backup generators.
The Human Side of Power Loss
Think about it: no lights during a stormy night, no way to charge phones to stay in touch, or a fridge full of food going to waste. It’s not just about inconvenience it’s about safety, comfort, and being prepared. A backup generator ensures your family stays secure and connected when the grid goes dark.
Types of Home Generators: What Are Your Options?
Portable Generators
Portable generators are the most budget-friendly option. You can move them as needed and use them to power specific appliances. They usually run on gasoline and are perfect for temporary or occasional use. However, they require manual operation and can't power your entire home.
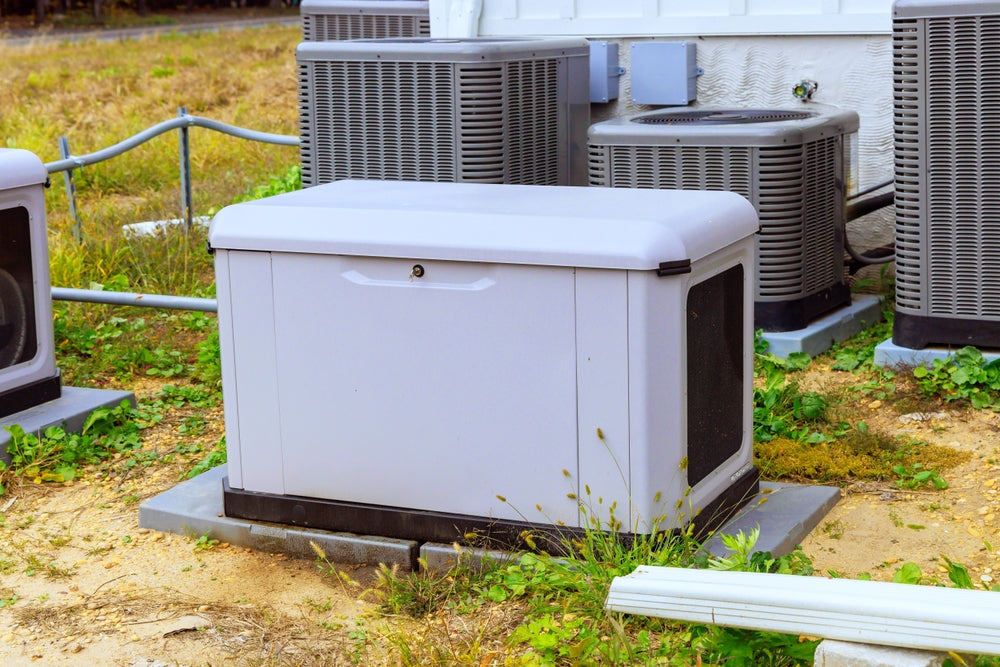
Standby Generators
Standby (or whole-home) generators are permanently installed outside your home. They automatically kick in when the power goes out. These models are more expensive but offer unmatched convenience and power capacity. They typically run on natural gas or propane and can support critical systems like HVAC, sump pumps, and kitchen appliances.
Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are a quieter, more fuel-efficient option. They adjust power output based on demand, making them ideal for sensitive electronics. However, they have lower output, which means they’re best suited for smaller homes or as secondary backup.
Calculating Your Home's Power Requirements
Start with a List
First, list the appliances and systems you want to power during an outage. Common essentials include the refrigerator, lights, Wi-Fi router, heating/cooling, and sump pump. Each of these has a wattage requirement.
Understand Running vs. Starting Watts
Some appliances require more power to start than they do to keep running. For instance, a refrigerator might need 1200 watts to start but only 200 watts to run. Add up both starting and running watts to find the minimum power output your generator must handle.
Fuel Types and What They Mean for You
Gasoline
Gasoline is easy to find, but it’s not ideal for long-term outages. It has a short shelf life and can be dangerous to store in large quantities. Also, gasoline generators can be loud and produce higher emissions.
Propane
Propane burns cleaner and stores better over time. Many homeowners opt for propane-powered generators due to its long shelf life and safer storage. However, propane generators usually have slightly lower output than gasoline-powered ones.
Natural Gas
If your home is already connected to a natural gas line, this is a fantastic option. It’s convenient and reliable, though it’s only viable if your area’s gas supply isn’t affected during emergencies.
Installation and Safety Considerations
Do You Need a Professional?
If you're installing a standby generator, the answer is yes. These systems must be connected to your home’s electrical panel and may require permits and inspections. A licensed electrician ensures everything meets local codes and safety standards.
Safe Operation Practices
Generators can be life-saving, but they also pose risks if used improperly. Never run a portable generator indoors or in a closed garage. Keep it at least 20 feet away from your home and direct the exhaust away from windows and doors. Always follow manufacturer guidelines.
Budgeting and Long-Term Value
Upfront Costs vs. Long-Term Peace of Mind
Portable generators may cost $400–$1,000, while standby generators typically range from $2,000 to $10,000 including installation. It’s a big jump, but consider the cost of hotel stays, spoiled food, or damaged electronics during blackouts. Over time, a standby generator often pays for itself in avoided hassle.
Warranties and Maintenance
Look for generators with solid warranties and available local service. Regular maintenance such as oil changes, filter checks, and test runs is essential to ensure your generator works when you need it most.
Final Thoughts: Make a Smart, Personalized Choice
Every home is different, and so are its backup needs. Whether you opt for a portable unit to keep the basics running or invest in a full-house standby system, the right generator gives you confidence and control.
Don’t just buy based on price or size consider your family’s habits, your area’s outage history, and how much peace of mind you want during an emergency.
Power might go out, but your comfort and safety don’t have to.