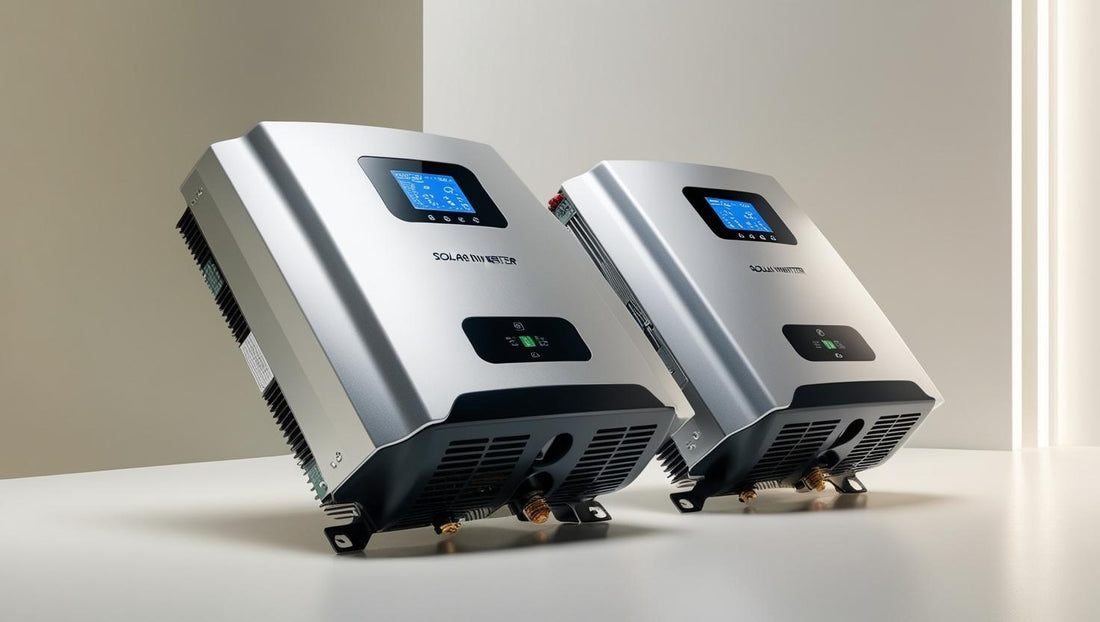
Solar energy is one of the best renewable energy sources available today. It helps reduce electricity bills, promotes sustainability, and is becoming more affordable with time. One of the key components of a solar power system is the solar inverter. It plays a crucial role in converting the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is used to power homes and businesses.
There are different types of solar inverters, each designed for specific needs and applications.
Powerhouse Express - A Trusted Name in Pakistan
Powerhouse Express is a leading Pakistani brand that provides high-quality solar inverters and other solar energy products. The company is known for its durable, efficient, and cost-effective inverters, making it a popular choice among homeowners and businesses looking to switch to solar power.
Key Features of Powerhouse Express Solar Inverters:
-
High Efficiency: Converts maximum solar energy into usable electricity.
-
User-Friendly Interface: Easy-to-use displays and controls.
-
Reliable Performance: Designed to handle the extreme weather conditions of Pakistan.
-
Affordable Solutions: Budget-friendly options without compromising on quality.
-
Wide Range: Offers different types of solar inverters for various applications.
Now, let’s explore the different types of solar inverters available in the market.
1. String Inverters
String inverters are the most common type used in residential and small commercial solar systems. They are connected to a series of solar panels, forming a "string."
Advantages:
-
Cost-Effective: Generally cheaper than other types of inverters.
-
Easy Maintenance: Since it is a single unit, maintenance is simpler.
-
Reliable Performance: Works well in locations with minimal shading.
Disadvantages:
-
Lower Efficiency in Partial Shading: If one panel in the string is shaded, the performance of all panels in the string is affected.
-
Limited Monitoring: Offers system-wide monitoring but not panel-level tracking.
2. Microinverters
Microinverters are small inverters installed on each solar panel instead of a single central inverter.
Advantages:
-
Maximum Power Output: Each panel operates independently, ensuring better performance.
-
Shade Tolerance: If one panel is shaded, it does not affect the others.
-
Panel-Level Monitoring: Allows real-time tracking of each panel’s performance.
Disadvantages:
-
Higher Cost: More expensive than string inverters.
-
Complex Installation: Requires more components, increasing installation time and cost.
3. Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters combine the functions of a solar inverter and a battery inverter. They allow solar energy to be stored in batteries for later use.
Advantages:
-
Energy Storage: Stores excess energy for use during nighttime or power outages.
-
Smart Energy Management: Can switch between solar, battery, and grid power automatically.
-
Better Efficiency: Optimizes energy usage based on demand.
Disadvantages:
-
Expensive: Costs more than traditional inverters.
-
Requires Batteries: Needs battery storage to utilize its full potential.
4. Off-Grid Inverters
Off-grid inverters are used in solar systems that are not connected to the main electricity grid. These inverters rely entirely on solar panels and battery storage.
Advantages:
-
Ideal for Remote Areas: Best for places without grid access.
-
Energy Independence: Users are not affected by grid failures or power cuts.
-
Works Well with Batteries: Designed to store and manage solar power efficiently.
Disadvantages:
-
High Initial Cost: Requires batteries, which add to the overall expense.
-
Complex Setup: Needs proper planning and installation.
5. Grid-Tied Inverters
Grid-tied inverters are designed to work with the main electricity grid. They do not require batteries and feed excess energy back to the grid.
Advantages:
-
Lower Cost: No need for expensive battery storage.
-
Net Metering Benefits: Excess electricity can be sent to the grid, reducing electricity bills.
-
Simple Design: Easy to install and maintain.
Disadvantages:
-
No Backup Power: Does not work during power outages.
-
Dependent on the Grid: If the grid fails, the system shuts down.
6. Central Inverters
Central inverters are similar to string inverters but are designed for large-scale solar farms and commercial applications.
Advantages:
-
High Efficiency: Designed for large power generation.
-
Cost-Effective for Large Systems: More affordable than using multiple string inverters.
-
Better Performance Management: Works well in controlled environments.
Disadvantages:
-
Not Suitable for Residential Use: Too large for home installations.
-
Single Point of Failure: If it malfunctions, the entire system is affected.
Choosing the Right Solar Inverter
When selecting a solar inverter, consider the following factors:
-
Energy Needs: Choose an inverter based on your electricity consumption.
-
Budget: Consider the upfront cost and long-term savings.
-
Grid Availability: If you have an unstable grid connection, a hybrid or off-grid inverter may be better.
-
Space and Installation: Some inverters require more space and complex installation.
-
Brand Reliability: Go for trusted brands like Powerhouse Express for quality and performance.
Conclusion
A solar inverter is an essential part of a solar power system. Whether you need a string inverter, microinverter, hybrid inverter, or an off-grid inverter, choosing the right one will ensure maximum efficiency and savings. Brands like Powerhouse Express offer excellent options for those looking for reliable solar solutions in Pakistan. By investing in the right solar inverter, you can enjoy clean, renewable energy and reduce your electricity costs for years to come.