In today’s digital age, electronics are everywhere from the fridge in your kitchen to the Wi-Fi router keeping your home connected. But here’s something we don’t think about until it’s too late: power fluctuations can damage these devices in an instant.
A voltage stabilizer acts like a bodyguard for your electronics, protecting them from sudden spikes, sags, and surges in electricity. Whether you're running a home office or just trying to keep your refrigerator safe, understanding how stabilizers work and when to use them can save you from expensive repairs or replacements.
Let’s explore what voltage stabilizers do, why they matter, and how to choose the right one for your home or business setup.
Why Power Fluctuations Happen More Often Than You Think
The Unseen Threat in Your Electrical Supply
We often assume the power coming into our homes is steady and safe. Unfortunately, that’s not always the case. Electricity supply can fluctuate due to poor wiring, grid overload, bad weather, or even faulty transformers. These fluctuations might last only a second, but they can have long-term consequences.
Voltage spikes can fry circuits. Voltage drops can wear down internal components. Even tiny, frequent changes in voltage called brownouts can silently shorten the life of your electronics over time.
Everyday Examples You Might Miss
Maybe your lights dim for a second when the air conditioner kicks in. Or your fridge starts buzzing louder than usual. These subtle signs often point to unstable voltage. Left unchecked, they can lead to permanent damage or shortened lifespans for your devices.
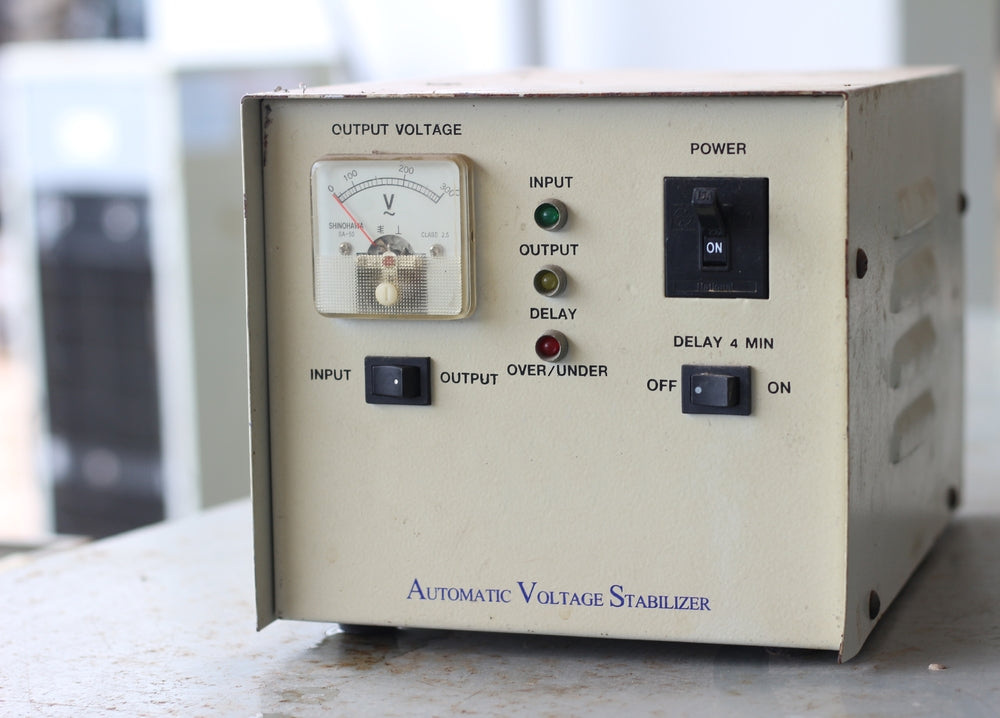
What Is a Voltage Stabilizer and How Does It Work?
The Basics, Explained Simply
A voltage stabilizer, sometimes called an automatic voltage regulator (AVR), maintains a consistent voltage level to your appliances, even when the incoming supply fluctuates. It does this by regulating and adjusting the voltage to a safe range before it reaches your devices.
This ensures that your electronics receive a steady, safe voltage level, whether the grid is delivering too much or too little.
Inside the Stabilizer
Most modern stabilizers use solid-state components, relays, and transformers to either boost or buck the voltage in real time. The result? Your TV, fridge, air conditioner, or computer receives the clean, uninterrupted power it needs to operate efficiently.
Types of Voltage Stabilizers
Manual vs. Automatic
There are manual stabilizers where users need to adjust voltage manually, but these are outdated and rarely used in modern settings. Today, automatic voltage stabilizers dominate the market. They detect fluctuations and adjust the voltage without any user intervention.
Servo vs. Relay vs. Static Stabilizers
-
Relay-based stabilizers are cost-effective and good for basic home use.
-
Servo-controlled stabilizers offer precise voltage correction, ideal for sensitive medical or industrial equipment.
-
Static stabilizers are digital and fast, often used in IT setups and data centers.
Each type serves a different purpose, so it’s important to match the stabilizer type to the application for optimal performance.
Where and When to Use a Voltage Stabilizer
Home Applications
Voltage stabilizers are commonly used for:
-
Refrigerators
-
Televisions
-
Air conditioners
-
Washing machines
-
Microwaves and ovens
-
Routers and modems
Appliances with motors or compressors are especially vulnerable to voltage changes, making stabilizers an essential addition.
Office or Commercial Setups
If you're running a small office or handling sensitive equipment like servers, stabilizers can prevent data loss, hardware burnout, and downtime. Even a desktop computer or printer can benefit from voltage protection, especially in areas with unstable supply.
How to Choose the Right Voltage Stabilizer
Match the Voltage Range
Your stabilizer should support the range of voltage fluctuations common in your area. For instance, if your grid often drops to 160V or spikes to 280V, choose a stabilizer that can handle that range.
Consider Load Capacity (kVA or Amps)
Each stabilizer is rated by how much load it can handle, typically in kilovolt-amperes (kVA) or amperes (A). Check the wattage or amperage of your appliance, then choose a stabilizer with a slightly higher rating to ensure safe operation.
Look for Additional Features
Modern stabilizers come with helpful features like:
-
Digital displays (showing input/output voltage)
-
Thermal overload protection
-
Time delay systems (to protect compressors)
-
Surge protection and noise filtering
These extras enhance both safety and usability, making them worth the slight premium.
Maintenance Tips to Keep Your Stabilizer in Shape
Keep It Dust-Free and Well-Ventilated
Overheating can affect stabilizer performance. Make sure it's placed in a dry, well-ventilated space and regularly wipe off dust and debris.
Check Performance Occasionally
Some stabilizers have self-test features. If yours doesn’t, monitor your appliances during brief voltage dips or spikes. If your device stays on without flickering, your stabilizer is doing its job.
Watch for Signs of Wear
Buzzing sounds, overheating, or frequent power trips could signal the stabilizer needs service or replacement. Don’t ignore these early warnings they could be protecting something much more expensive.
Final Thoughts: Small Device, Big Protection
We often think of surge protectors and power strips as enough. But in areas with frequent voltage fluctuations, a voltage stabilizer is your real first line of defense.
It's a relatively small investment, but it guards thousands of dollars’ worth of electronics. Whether you're protecting a smart TV, a home theater system, or your company’s server rack, stabilizers provide peace of mind in a world where electricity is never as stable as we hope.
Think of it this way: you lock your doors at night. Why not protect your electronics too?