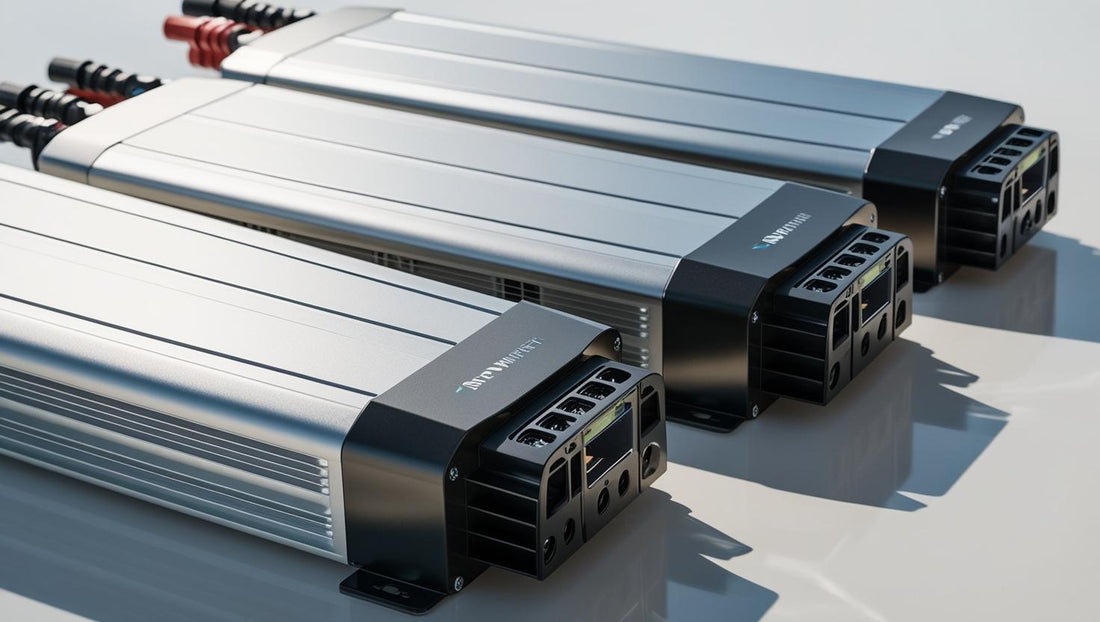
Understanding Solar Inverters
Every solar power system relies on a crucial component called a solar inverter. At its core, a solar inverter converts the direct current (DC) electricity produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity—the form used by virtually all household appliances and the electrical grid. Without an inverter, the energy captured by your panels would remain unusable within most modern homes.
Key Functions of a Solar Inverter
-
DC to AC Conversion
Solar panels produce DC electricity. The inverter’s primary role is to invert this DC into AC, matching the voltage and frequency (usually 230 V at 50 Hz in Pakistan) required by residential systems. -
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
Inverters continuously adjust their input to operate solar panels at their “maximum power point.” This dynamic tuning ensures you extract the highest possible power from your panels throughout the day, even as light conditions change. -
Grid Synchronization and Safety
For grid-tied systems, inverters synchronize the phase and frequency of the generated AC with that of the utility grid. They also incorporate safety features—such as anti-islanding protection—to automatically shut down in case of a power outage, safeguarding utility workers and preventing backflow into the grid.
Types of Solar Inverters
-
String Inverters
The most common type, string inverters connect a series (“string”) of solar panels to a single inverter. They’re cost-effective but can suffer output loss if one panel underperforms due to shading or soiling. -
Microinverters
Installed beneath each panel, microinverters optimize output on a per-panel basis. While more expensive upfront, they minimize the impact of localized shading and simplify system expansion. -
Hybrid Inverters
Also known as multi-mode inverters, these units combine the functions of a solar inverter and a battery charger, allowing seamless integration of on-grid, off-grid, and battery backup capabilities.
How Does a Solar Inverter Work?
-
Power Harvesting
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity. That DC is then routed to the inverter via wiring. -
Inversion Process
Inside the inverter, semiconductor switches (typically IGBTs or MOSFETs) rapidly switch the DC input on and off, creating a pulsed waveform. Sophisticated filters then smooth this into a clean, sinusoidal AC output. -
Optimization via MPPT
Simultaneously, the inverter’s MPPT controller monitors voltage and current at the panel terminals. It adjusts its input parameters to ensure the panels operate at their most efficient voltage point, which varies with sunlight intensity and temperature. -
Synchronization with the Grid
For grid-connected installations, the inverter constantly compares its AC output to the grid’s frequency and phase. It fine-tunes its switching to keep both perfectly in sync, enabling safe and efficient energy export or import. -
Monitoring and Diagnostics
Modern inverters include built-in monitoring systems that track performance data—such as daily yield, voltage, and fault codes—and often provide real-time access via web portals or mobile apps.
Leading Brands: Knox Inverter and Inverex Inverter Pricing
When choosing an inverter in Pakistan, reliability and after-sales support are just as important as technical specs. Knox Inverter is one emerging name known for offering pure sine-wave output, advanced MPPT, and robust thermal management. Their units often include user-friendly LCD panels for on-site diagnostics, making them a solid choice for homeowners seeking both performance and ease of operation.
Meanwhile, Inverex is one of Pakistan’s largest solar brands, renowned for its extensive range of on-grid and hybrid inverters. Prices for Inverex inverters in Pakistan vary widely depending on capacity and features—from compact 800 VA models to commercial-grade 20 kW three-phase units. Across major online retailers, you’ll find Inverex inverter prices ranging from as low as PKR 2,500 up to PKR 1,260,000, with an average market price around PKR 284,000
Choosing the Right Inverter for Your Needs
-
System Size
Match inverter capacity to your solar array’s output. Undersizing can lead to clipping (lost energy), while oversizing reduces efficiency and raises costs. -
Future Expansion
If you plan to add panels or batteries later, consider a hybrid inverter or a modular microinverter setup that scales with your needs. -
Warranty and Support
Look for inverters with at least a 5- to 10-year warranty, and verify that local service centers can handle repairs or firmware updates. -
Efficiency Ratings
Inverters with peak efficiencies above 97% will waste less energy during conversion, boosting your overall return on investment.
Conclusion
A solar inverter serves as the heart of any photovoltaic system, transforming the sun’s DC output into clean, usable AC power while optimizing performance through MPPT and safeguarding your installation. Brands like Knox Inverter offer innovative features for residential users, while established names such as Inverex provide a broad spectrum of reliable inverters—priced in Pakistan from PKR 2,500 to PKR 1,260,000. By understanding how inverters work and evaluating your specific needs, you can select a unit that maximizes your solar harvest and secures long-term energy independence.